Empowering Makers through Digital Maker Passports
- January 29, 2025
- 5 min read
Internet of Production envisions a future defined by open, shared knowledge and decentralized, locally driven manufacturing. By connecting people, skills, and resources globally, they empower communities to create solutions that meet their unique needs while leveraging global expertise. This vision is at the heart of their involvement in the mAkE consortium where they are leading the work on technical innovative infrastructures developed as part of a distributed manufacturing network defined in work package 4 of the mAkE project.
Watch the Maker Passport mAkE talk here:
Creating Technical Infrastructure for Distributed Manufacturing

Under the mAkE project, we have spearheaded the development of innovative infrastructures supporting a distributed manufacturing network. Work Package 4 focuses on integrating key components of distributed manufacturing, including business models, geographic data, and contracting mechanisms. The goal is to establish an interoperable network that positions digital innovation hubs (DIHs) as drivers of local production across Africa and Europe.
Skills in Focus: The People and Skills Data Specification
A crucial aspect of Work Package 4 is the development of a data specification that creates a framework for communicating production-related and manufacturing skills. This specification acts as a shared language, enabling makers to clearly articulate their expertise and making it easier for clients and collaborators to find the right talent for their projects.
The Digital Maker Passport
At the core of this shared language is the Digital Maker Passport. This tool connects makers across a global ecosystem of digital innovation hubs. By standardizing the way skills and experiences are documented, the Maker Passport facilitates:
- Efficient collaboration by enabling individuals and organizations to find skilled makers.
- Rapid prototyping through the seamless exchange of expertise.
- Higher-quality production driven by access to verified skill sets.
Research Behind the Data Specification
The People and Skills Specification, which is publicly available on the open publishing platform PubPub, was developed through extensive community-centered research, including:
- Document analysis to identify existing frameworks.
- Interviews with makers and makerspace leaders to understand practical challenges.
- Surveys to gather broader input from the maker community.
This research led to the creation of a shared taxonomy of skills and experiences, which is foundational to expanding the global network of makers and empowering local communities to engage in product prototyping and manufacturing.
How the Digital Maker Passport Works
The Maker Passport builds on the People and Skills Specification to document and verify an individual’s skills, training, and certifications. Two methods have been identified as pathways for turning skills into digital certificates.
Method 1: Community-Based Authentication
One pathway for creating digital certificates involves community-based authentication. In this approach, makerspaces act as certificate issuers, verifying skills and training based on their own standards. This method ensures:
- Data sovereignty, as credentials are issued within a closed, independent system.
- Flexibility, allowing makerspaces to tailor certifications to their unique programs, such as apprenticeships or specialized training.
For example, a makerspace might issue certificates for skills like 3D CAD, generative design for additive manufacturing, or specific safety protocols. These certificates can range from beginner to expert levels, depending on the issuing organization’s determination.
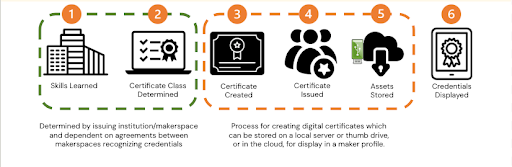
The process of creating a digital certificate involves several steps:
- Certificate Generation: A makerspace inputs details about the skill or training, which is then validated using tools like Python or XML.
- QR Code Creation: A QR code is generated and either printed or displayed digitally.
- Identity Verification: The maker signs the QR code using a personal device or through manual verification by the issuer.
- Final QR Code Issuance: The issuer countersigns the certificate, generating a final QR code that serves as the digital certificate.
This QR code can then be stored on a secure device or in a Solid App – a decentralized personal data store that ensures privacy and control. Makers can use these certificates to verify their skills when collaborating with clients or accessing specialized equipment.
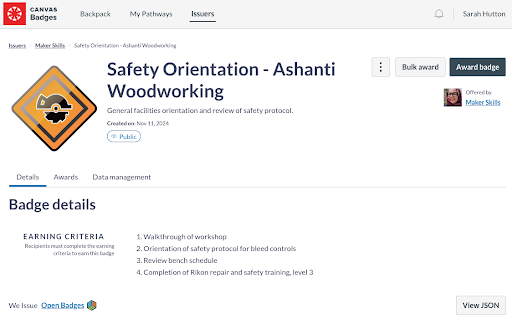
Method 2: Pre-Existing Badging Systems
For organizations already using badging platforms, such as Canvas Badges (formerly Badgr), the People and Skills Specification can be integrated to create digital badges. These badges clearly define the skills and training represented, using the shared vocabulary of the specification.
Practical Use Cases of the Maker Passport
The Maker Passport is already being tested and refined through various initiatives:
Distributed Manufacturing Trials in Africa
Through the Innovative Manufacturing in Africa 2023 Project, funded by Research and Innovation Systems for Africa (RISA fund), we worked with makerspace communities in Kenya, Ghana, and South Africa. During the distributed manufacturing trials run, we gathered feedback on the Maker Passport and tested its use in producing local healthcare products for community organizations.

Makers at a recycling station at the Makerspace Durban, 2023. Credit photo: The Makerspace Durban
Collaboration with H-FABLAB and REFFAO
In partnership with REFFAO and H-FABLAB, we are developing a proof of practice for using the People and Skills Specification to:
- Document training programs and workshops.
- Bundle education materials with digital certificates, demonstrated through the OKH Solid App.
These efforts aim to refine the process of capturing and sharing maker skills while ensuring alignment with community needs.
Building a Global Network of Makers
The ultimate goal of the Maker Passport and the People and Skills Specification is to create a global network of connected makers. A dedicated platform allows makers to:
- Showcase their skills and certifications.
- Connect with collaborators and clients.
- Access resources and training through digital innovation hubs.
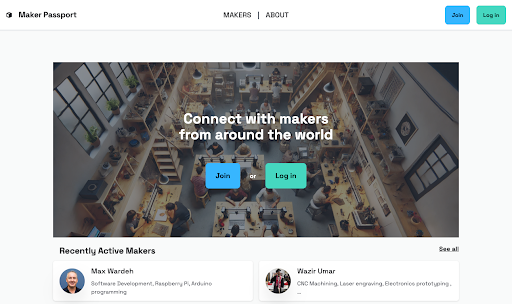
https://maker-passport.fly.dev
All tooling developed for this platform is open source, encouraging community contributions and collaboration.
Get Involved
We invite you to join the conversation and contribute to the future of distributed manufacturing. Visit the Internet of Production’s community forum to share your ideas and learn more about ongoing projects. Together, we can build a world where open, local production is accessible to everyone.
People and Skills Working Group: https://shorturl.at/F36nR
People and Skills Channel https://shorturl.at/B4XQe
Internet of Production on Github https://github.com/iop-alliance
Maker passport presentation is available here:
















